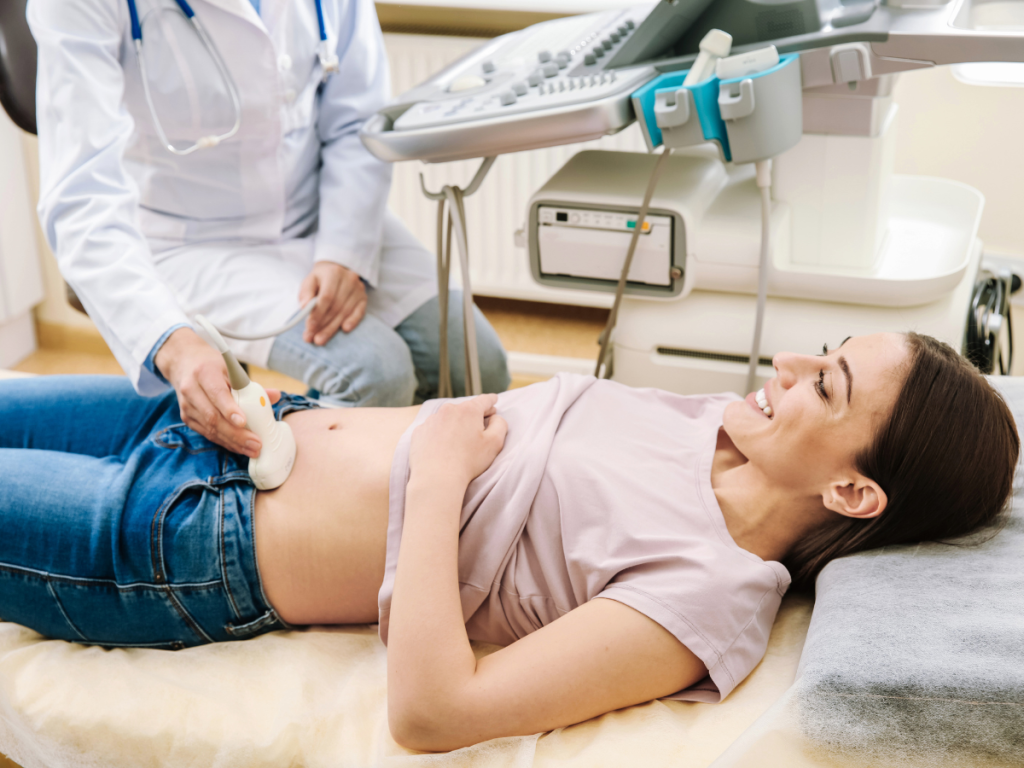
Transvaginal ultrasound is a medical procedure that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to capture images of the pelvic region. It is commonly used by gynecologists to assess reproductive organs and diagnose a variety of conditions. In this article, we will address common questions about transvaginal ultrasounds, their purpose, procedure, and benefits.
What is a Transvaginal Ultrasound?
A transvaginal ultrasound, also known as endovaginal ultrasound or pelvic ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging technique that involves inserting a small probe into the vagina. The probe emits sound waves that bounce off the organs and tissues in the pelvic area, creating detailed images on a monitor. This procedure allows healthcare professionals to examine the uterus, ovaries, cervix, and nearby structures.
Why Do You Need a Transvaginal Ultrasound?
Transvaginal ultrasounds serve various purposes, including:
-
Evaluating Reproductive Health: Gynecologists often use transvaginal ultrasounds to assess the health of the reproductive organs. It helps identify abnormalities, such as cysts, fibroids, or polyps, which can affect fertility or cause discomfort.
-
Pregnancy Monitoring: Transvaginal ultrasounds provide detailed images during early stages of pregnancy when a traditional ultrasound might not capture clear images. This helps monitor fetal development, detect ectopic pregnancies, or diagnose potential complications.
-
Infertility Assessment: For couples experiencing difficulties conceiving, transvaginal ultrasounds can provide valuable insights into potential causes. It helps identify conditions like endometriosis, uterine abnormalities, or ovarian cysts that may impact fertility.
-
Post-menopausal Monitoring: Women who have reached menopause might require transvaginal ultrasounds to monitor the thickness of the endometrium (lining of the uterus). Abnormal thickness can indicate conditions such as endometrial hyperplasia or cancer.
How is a Transvaginal Ultrasound Performed?
A transvaginal ultrasound is a relatively straightforward procedure. Here’s what you can expect:
-
Preparation: You will be asked to empty your bladder before the procedure. This ensures a clear view of the pelvic area.
-
Positioning: You will lie on an examination table with your feet in stirrups, similar to a pelvic exam.
-
Lubrication and Insertion: The ultrasound probe, covered with a protective condom and lubricant, is gently inserted into the vagina. The lubrication minimizes discomfort.
-
Imaging: The technician moves the probe within the vagina to capture different angles and images of the reproductive organs. The images appear on a monitor in real-time.
-
Completion: Once the necessary images are obtained, the probe is gently removed, and you can resume regular activities immediately.
Is a Transvaginal Ultrasound Painful?
Many women wonder about the discomfort associated with a transvaginal ultrasound. While individual experiences may vary, the vast majority of patients only experience minimal discomfort or pressure during the procedure. The use of lubrication and the technician’s gentle movements help reduce any potential discomfort.
Benefits of Transvaginal Ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasounds offer several advantages over traditional abdominal ultrasounds. These include:
-
Higher Resolution Imaging: Due to the close proximity of the probe to the pelvic organs, transvaginal ultrasounds produce clearer and more detailed images than traditional ultrasounds.
-
Increased Sensitivity: The proximity of the probe enables better detection of small abnormalities, providing valuable information to healthcare professionals.
-
Early Detection: Transvaginal ultrasounds can detect potential issues at an earlier stage, increasing the chances of successful treatment and improved outcomes.
Conclusion
Transvaginal ultrasounds are valuable diagnostic tools that play a crucial role in assessing reproductive health, monitoring pregnancies, and identifying potential issues. With minimal discomfort and higher-resolution imaging, this procedure offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers.
| Keywords |
|---|
| Transvaginal ultrasound |
| Pelvic imaging |
| Reproductive health |
| Early pregnancy monitoring |
| Infertility assessment |
Titles:
- Understanding Transvaginal Ultrasounds: A Comprehensive Guide
- Transvaginal Ultrasound Explained: Everything You Need to Know
- The Importance of Transvaginal Ultrasounds in Reproductive Health
- Early Pregnancy Monitoring with Transvaginal Ultrasound
- Investigating Infertility: How Transvaginal Ultrasounds Can Help
In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of kidney scans and provide answers to some frequently asked questions in relation to this diagnostic procedure. A kidney scan, also known as renal scan, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique used to assess the structure and function of the kidneys. Whether you are a patient seeking further information about kidney scans or a healthcare professional looking to enhance your knowledge, keep reading to find out more.
- What is a kidney scan?
A kidney scan is a diagnostic procedure that utilizes radioactive tracers and specialized equipment to create images of the kidneys. These images help healthcare professionals evaluate the structure and function of the kidneys, detect abnormalities, and identify potential underlying conditions affecting renal health.
- Why is a kidney scan performed?
A kidney scan may be performed for various reasons, including:
-
Assessing kidney function: The scan can determine how well the kidneys are working, their filtration rate, and the overall blood flow to this vital organ.
-
Detecting abnormalities: Kidney scans can identify abnormalities such as kidney stones, cysts, tumors, or blockages in the urinary tract.
-
Evaluating infection or inflammation: In cases of suspected infection or inflammation of the kidneys (such as pyelonephritis), a kidney scan can provide valuable information for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
-
Monitoring post-treatment progress: Patients who have undergone kidney-related surgeries or treatments may require regular kidney scans to monitor their progress.
- How is a kidney scan performed?
During a kidney scan, a small amount of a radioactive tracer substance, such as technetium-99m, is injected into the patient’s bloodstream. This substance is primarily eliminated through the kidneys, allowing healthcare professionals to track its movement using a specialized camera or scanner. The scanner captures images that illustrate the distribution and excretion of the tracer within the kidneys, providing valuable insights into their structure and functionality.
- Are kidney scans safe?
Kidney scans are generally considered safe, posing minimal risks to patients. The radioactive tracer used in the procedure emits a very small amount of radiation, which is within safe limits. However, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, as special precautions may need to be taken to protect both you and the developing fetus or infant from unnecessary radiation exposure.
- How should one prepare for a kidney scan?
Preparation for a kidney scan may vary depending on the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider. In general, it is advisable to:
- Inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions or allergies you may have.
- Provide a list of medications you are currently taking.
- Wear comfortable clothing and remove any metallic objects, such as jewelry, before the procedure.
- Follow fasting guidelines, if required, as specified by your healthcare provider.
- What can be expected during a kidney scan?
During a kidney scan, patients lie on an examination table while a technician operates the scanner or camera. You may be asked to change positions during the procedure to obtain different angles for imaging. The scan itself is painless and typically lasts for about 30-60 minutes. Patients are advised to remain still and relaxed, as movement can blur the images.
- Are there any potential side effects or complications?
Kidney scans are generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects or complications. However, some patients may develop a mild allergic reaction to the radioactive tracer. It is essential to notify the healthcare provider if you experience any significant discomfort, pain, or unusual symptoms during or after the procedure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a kidney scan is a valuable diagnostic tool used to assess the structure and function of the kidneys. This non-invasive procedure aids in detecting abnormalities, evaluating kidney function, and monitoring treatment progress. By understanding the basics of kidney scans and addressing common concerns, patients can approach this diagnostic test with confidence and actively participate in their healthcare journey.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts and questions in the comment box below. Don’t forget to share this article with your friends who may find it useful.
Meta Tag Keywords: kidney scan, renal scan, kidney function assessment, kidney abnormalities, kidney health diagnosis
Meta Titles:
- Kidney Scan: A Comprehensive Guide to Assessing Kidney Health
- Understanding Renal Scans: Everything You Need to Know
- Decoding Kidney Scan: Unraveling the Secrets of Renal Health
- Demystifying Kidney Scans: What You Should Expect
- Kidney Scan Explained: Insights into Assessing Renal Function